Highlights
Kiwi.com: Nonstop Operations with Scylla Even Through the OVHcloud Fire
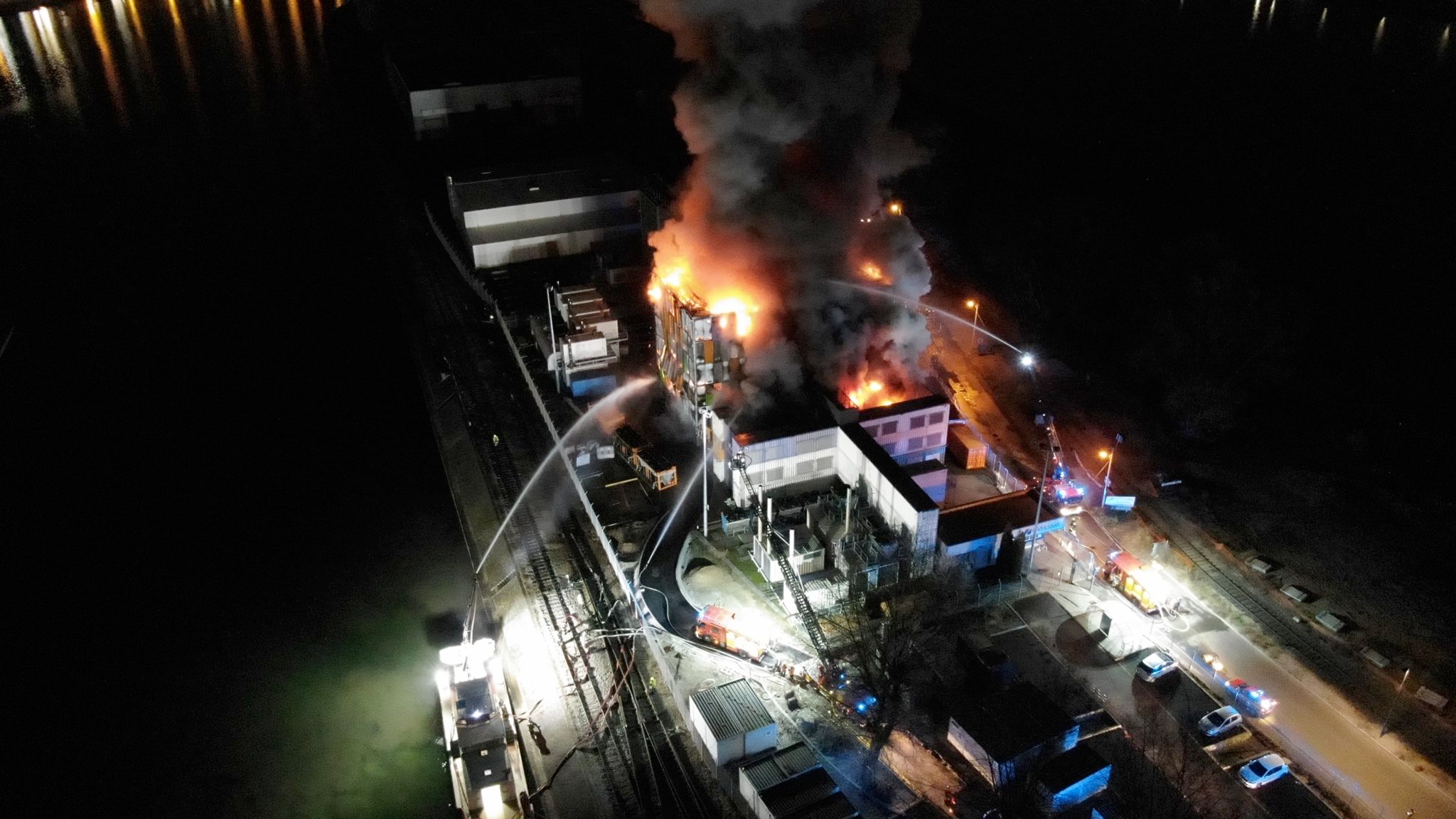

Fire on French OVHcloud affected four datacenters: SBG2 was destroyed, SBG1 adjacent rooms were partially on fire, SBG3 and SBG4 were switched off to fight the fire. Overall, 3.6 million websites were affected, including banks and mail servers.
Kiwi.com uses Scylla - NoSQL database, as a highly available and resilient solution. Their monitoring system detected spikes as nodes went down but later other OVHcloud datacenters took over the requests. 10 out of 30 nodes became unavailable, however, Scylla cluster was able to rebalance. Their load shifted from 25% to 30-50%. Scylla is datacenter topology aware, so copies of data were geographically distributed. Having multiple copies of data is expensive but having resilience in such situations is priceless.
Kiwi.com designed their architecture that datacenters are located at least 200 km away. Scylla database is replicated in three datacenters, synchronized via OVH private network. Scylla cluster was sized in a way to be able to handle additional load.
Vrbo: Mongo Change Streams for Real-Time Notifications
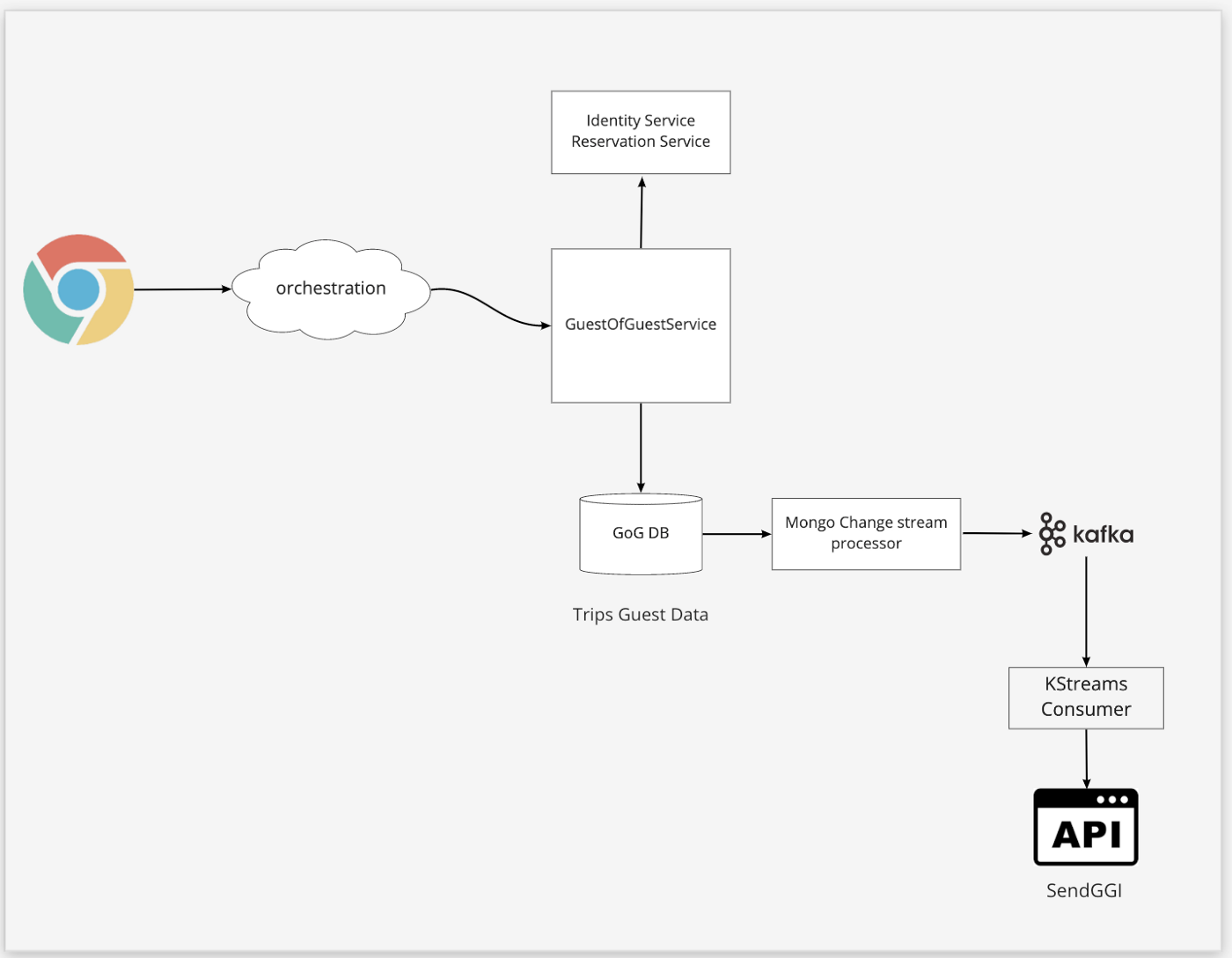
Vrbo is a travel booking service. After the booking, user can invite other guests to their trip. Such information is stored in MongoDB document. MongoDB Change Streams uses oplog to get document updates. A special microservice processes such updates and publishes appropriate events to Kafka, so user can get notifications etc.
Each stream event has a unique ID. Microservice persists this ID in a separate MongoDB collection. If an application was disconnected from the stream, it can use this ID to get all the events that were missed since the disconnect happened.
Couchbase: How we implemented Distributed Multi-document ACID Transactions
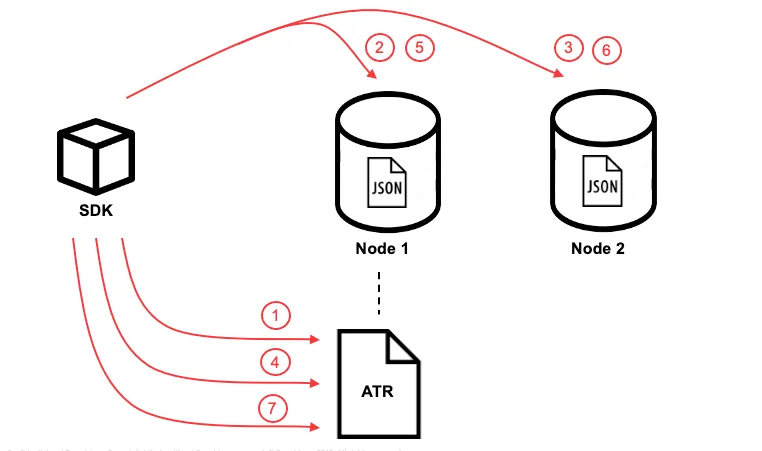
This blog post describes the implementation of distributed transactions in Couchbase, where documents should be updated on different shards in one transaction in NoSQL system. Couchbase has a leaderless architecture. There is no central coordinator. SDK stores a copy of a cluster map. Couchbase uses CRC32 hashing algorithm. Having cluster map and hashed document key, SDK can immediately find the responsible shard. Effectively, each application instance is a coordinator on its own.
The transaction mechanism is implemented on SDK end. Each shard (called vBucket) maintains Active Transaction Record (ATR). On transaction start, a new entry is added to ATR (just one ATR per transaction is used). Then, content on Node1 is being updated and marked as staged in the metadata. Other nodes are mutated the same way. On the next step, transaction is marked as committed in the ATR. Then, the metadata for the documents is updated as unstaged on all participated nodes. Finally, transaction is marked as completed in ATR.
What if we want to read the data after the transaction is committed but before changes are unstaged? If the client received a staged document, it checks it against ATR, and sees if it was committed.
The data is replicated memory-to-memory, which is quick. The fasted way is to respond that the write was successful on a single node, if it’s acceptable to loose some data. There is a chance that a node goes down before it replicates its data to other replicas. Otherwise, it’s possible to set different durability level, for example Majority level. In this case the write is acknowledged against majority of nodes, which slows down the response but doesn’t violate ACID principles.
The Journey from Batch to Real-time with Change Data Capture
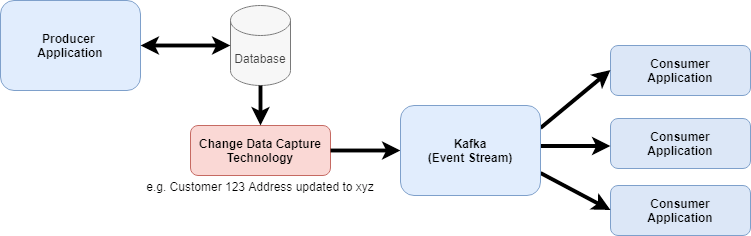
This article explores Event Sourcing coupled with Change Data Capture (CDC). CDC reads transaction log of the database and streams changes to another source, typically Kafka. Such transactions are considered as immutable events that can be replayed as per Event Sourcing. Kafka persists all events and doesn’t delete them after they were delivered to consumer, hence it is a good technology for Event Sourcing. Good use case for CDC is transforming a monolith into microservices.
Two common technologies for CDC are Debezium and AWS DMS (Data Migration Service). Latter was originally created as customers migration tool for AWS, it supports all major database engines. Debezium is an open source technology. It can be used to stream events to Kafka which will then be sent to various sources. Debezium also has a set of various connectors to various destinations. In this case, Debezium keeps updates in memory.
Grafana: How we responded to a 2-hour outage in our Grafana Cloud Hosted Prometheus service
Grafana Cloud onboarded a new customer to their multi-tenant Prometheus cluster. This new customer mistakingly started sending more data than expected. Although, appropriate limits were correctly set, there was a bug that prevented blocking extra requests from the tenant. Extra load overwhelmed the cluster resulting in cascading failures across the stack. It turned out that fail-path was more CPU-intensive than success-path. Authentication gateways became overloaded and were removed by load balancers. Scaling up the cluster didn’t help. Grafana eventually identified the tenant that caused the overload. Stricter limits were applied which solved the issue.
Overall, outage lasted around 2 hours. The limits bug was eventually fixed. Limits automation was implemented along with cluster management improvement. The team is also working on recreating the scenario on dev environment.
Product News
Open sourcing Querybook, Pinterest’s collaborative big data hub
Advancing connectivity between the Asia-Pacific region and North America
System Design
Software Architecture
Using Context to Improve Intent Classification in Walmart’s Shopping Assistant
Predict It! An Engineer’s Journey into Data Science
Building Smarter Search Products: 3 Steps for Evaluating Search Algorithms
Compiling Containers – Dockerfiles, LLVM and BuildKit
Application of Semi-Supervised Neural Net to eCommerce Image Classification
Examining Problematic Memory in C/C++ Applications with BPF, perf, and Memcheck
Culture
Anatomy of a Targeted Ransomware Attack
How We Enable Airbnb Team Members to Code Like a Mobile Engineer