Highlights
FullContact: Improving the Graph: Transition to ScyllaDB
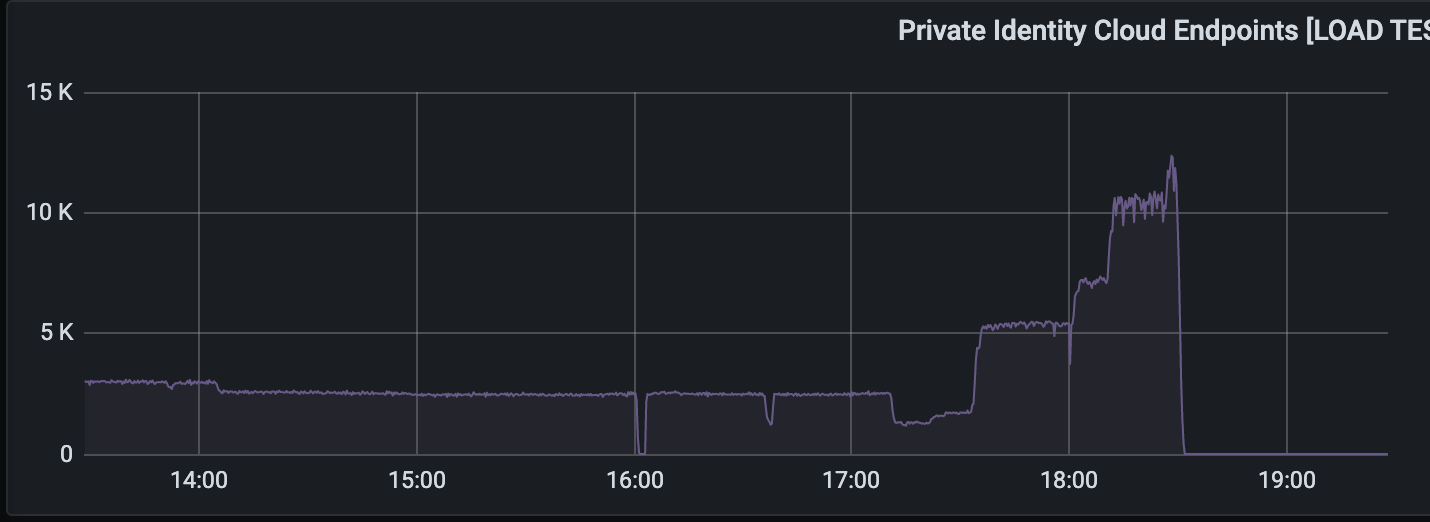
FullContact set an ambitious goal of 10,000 QPS. Initially, they moved their database from HBase to Cassandra. Cluster consisted of 3 instances of c5.2xlarge EC2 + 2 TB of gp2 EBS storage. With the growing amount of records in the database, response time crept from 100 ms to 300 ms. It turned out that the default Size Tiered Compaction Strategy is optimized for inserts which lead to a single file for SSTable. As a consequence, it maxed out the 250 MB/s limit for EBS.
As an optimization, it was decided to switch to Leveled Compaction Strategy. This temporarily solved the problem. The next step was to double the heap size for the database. Also, they reduced SSTAble size to 80 MB. After all optimizations, the performance grew to 3,000 QPS.
Next, the FullContact team started experimenting with Scylla, which is Cassandra compatible to extent that SSTable files are in the same format. Comparing to Cassandra’s start-up within a seconds after copying the database files, it took Scylla hours to re-compact large database tables. After that, the API was finally able to handle more than 10,000 QPS, peaking to 20,000 QPS with 98p under 50 ms. Scylla supports Prometheus metrics, has preconfigured Grafana dashboards. The cluster was provisioned with 8 nodes of c5.large EC2.
Behind GitHub’s new authentication token formats
GitHub updated its authentication tokens format. Key takeaways:
- Add prefix to make token identifiable. In the case of GitHub it’s a 3 characters prefix that starts with
ghand another letter for a token type, for example,gho- OAuth token,ghs- server-to-server token, etc. - Use underscore separator:
_. It improves readability and easy to copy with a double click. - Use the last 6 digits as a checksum. It helps as a first step of the validation without even requesting the database.
Load Balancing in Scylla Alternator
Scylla supports DynamoDB API through Alternator. While clients that work with CQL (Cassandra Query Language, also supported by Scylla) are fully aware of different DB nodes, DynamoDB is a cloud solution that looks like a single URL, for example, https://dynamodb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com. There are multiple nodes behind this URL, so there is a load balancer in front of them.
DNS load balancing returns different IP addresses with 5 seconds TTL for each request. This solution is very efficient because only DNS data goes through the server. If a node becomes unavailable, another node can pick up its IP address. This is called the floating address technique.
The above server-side solution works well for the cloud but is more complex for Scylla users that are responsible for the deployment of their DB. An alternative is client-side load balancing. In this case, the application uses the Alternator discovery service to get the list of available nodes. As a downside, it requires multiple changes to the application. To avoid that, there is an SDK that can be added as a library to the application. The blog post contains an example in Java, other languages are also supported.
MySQL: InnoDB Data Locking – Part 4 “Scheduling”
After the database engine finished processing a transaction, which transaction should be picked up next? For years MySQL engine InnoDB was using First In First Out queue (FIFO) until researchers from the University of Michigan published a paper proposing a better way to choose the next transaction.
It turns out that FIFO doesn’t take into account the transaction age in the system because a transaction can request access to different resources over its lifetime and it will be considered as new in different queues. Proposed Variance Aware Transaction Scheduling had to solve this problem by rearranging waiters by the birth date, however, it never made it to production because researchers came up with the new paper that takes this idea further: Contention-Aware Lock Scheduling (CATS).
The idea is to sort transactions based on the number of other transactions that have to wait if this transaction is waiting. To determine this number, a wait-for graph should be built. Traversing such a graph is not as straightforward as it may seem. There are also some performance considerations. The weight value is not calculated on the fly, instead, it uses a snapshot of wait-for relations which is processed in a separate thread. The final version has some optimizations and doesn’t strictly traverse the graph in a topological order but is good enough from a performance perspective. It’s available in MySQL as of version 8.0.3
Uber: Making Changes Quickly and Safely at Scale (Flipr)
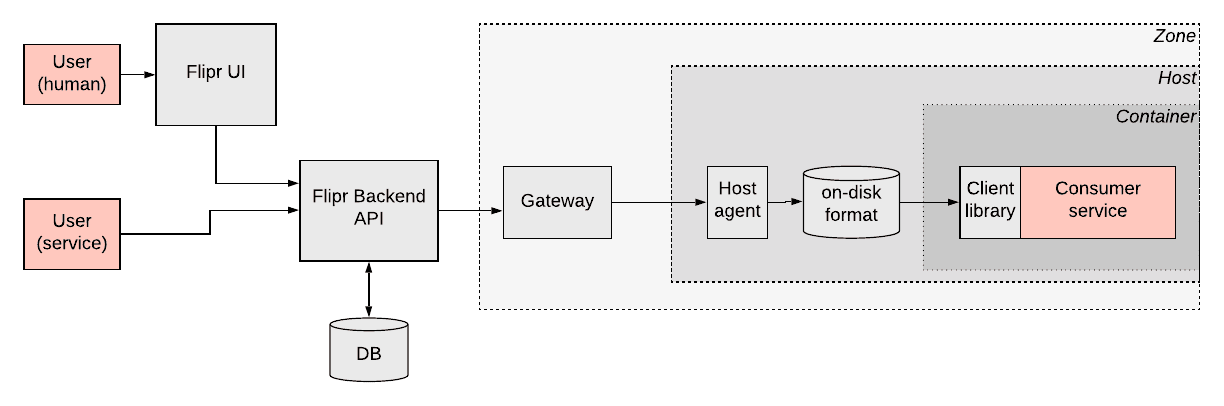
Applications usually need their configuration passed in a form of a boolean feature flag or other values like an integer for max number of characters. Uber faced a challenge that such configuration should also depend on different sort of condition. For example, enable a particular feature only in a particular city. In other words, configuration depends on context. Also, some parameters are only known for the application in runtime.
Uber team designed a system called Flipr that solves this problem. A client library gets the configuration from the Flipr API. Uber infrastructure is so massive that this API uses caching. In the future, a subscription model will be able to deliver config to the apps. The host agent persists data on disk, so in case of any failure, an application can still read its config.
Any configuration changes require peer reviews. There is also access control and permission system to ensure only authorized people get access to the configuration. Config rollouts can be done incrementally with monitoring and automatic rollback if necessary. 700 services on 50K hosts at Uber use Flipr. This generates a load of about 50K QPS.
Product News
Cloudflare Pages is now Generally Available - Pages is another solution to build static websites. Taking it further with Workers and Durable Objects, it opens possibilities to create full-stack services.
Location-based personalization at the edge with Cloudflare Workers - I thought it’s nice that Cloudflare picked my city as an example of location-based personalization with Cloudflare Workers. And then I realized it shows me how it works. Awesome!
Live stream to multiple platforms with Stream Connect - Interesting case. Cloudflare allows streaming to the nearest edge server which will then re-stream video to Youtube, Facebook, and Twitch.
System Design
Kubernetes As Explained Through the 1997 Blockbuster Titanic - What if Titanic was run with Kubernetes? This article will not teach you k8s but it’s fun to read.
Improving the Graph: Transition to ScyllaDB
Tutorials
Learn how to monitor your energy use at home with a Raspberry Pi, Grafana and Prometheus - Turns out it’s pretty easy to build an energy consumption monitoring for a smart home. I might build it at my home.
Culture
Rethinking Spotify Search - Spotify’s struggle with search. At some point, there were about 5 different search teams concentrated on different parts of search, like ingesting data, API, etc.
Achieving Insights and Savings with Cost Data - Airbnb built an entire system to monitor and control their AWS costs, so they can reach out to stakeholders internally and reduce unnecessary usage and save money.