Highlights
Managing Asynchronous Workflows with a REST API
Building a REST API, sometimes there is a need to run some complicated logic that takes some time. In these cases, the REST call sparks an asynchronous job.
For example, a call to generate a PDF report: POST /api/v1/report. In response, REST API answers with status HTTP/1.1 201 Created and a Location header to get the result Location: /api/v1/report/123.
What are the options to fetch the result of this asynchronous job?
The first option is Polling. The best practice to constantly poll the resulting URL with the exponential backoff until it returns the job run result. Some maximum intervals should be set to avoid indefinite polls. This is a simple pattern however it puts more complexity on the client-side, wastes resources for polling, and the response time is not optimal.
The second option is Webhooks. The webhook URL will be called at the end of the job to deliver the result. Such webhook URL should be predefined as an initial configuration of the client or can be provided as a part of the initial request. This is a good option for server-to-server communication. This strategy delivers fast notification but requires extra effort to register a webhook. In addition, the caller must host an API endpoint. Alternatively, notifications can be sent via email or SMS to the user.
Another option is WebSocket API. In most cases, it’s used with browser-based clients. The initial REST API response contains a WebSocket API URL. A client starts listening to this URL and the server pushes notification as soon as the job is done. This strategy is the most complex to implement.
It’s worth noting that GraphQL has a subscription operation type to subscribe to operation results.
Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part IV: Multi-site Active/Active
We’ve discussed various disaster recovery strategies in Issue 006 of System Design Weekly. Let’s review active/active strategy in more detail.
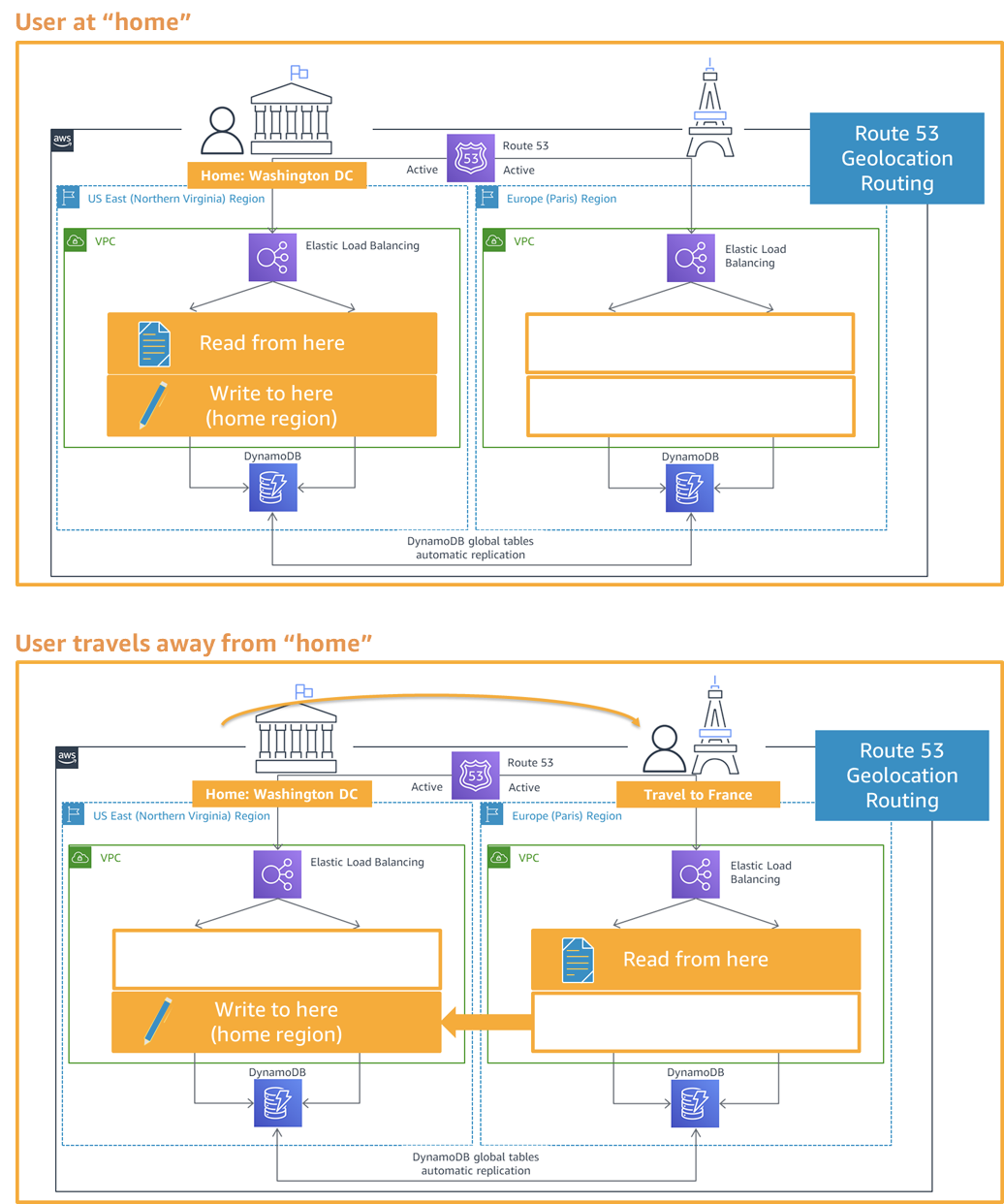
With the active/active multi-site strategy, the workload is spread across several AWS Regions, each one containing multiple availability zones. The data is replicated and backed up. Each region serves the production traffic. The traffic is routed between regions based on geolocation or latency policies by Route53, a cloud DNS by AWS.
With read local/write local pattern, each request is routed to a local region for lower latencies. Writes to the local region are replicated to other regions. In case if DynamoDB global tables replication is subsecond and the last write wins in case of concurrent updates.
With the read local/write global pattern, one Region is chosen to be global. Locally received writes should be redirected to the global Region. In the case of Aurora global database, a primary cluster is deployed to the global Region with read-only replicas deployed to other Regions. The data is usually being replicated in under a second. Aurora global database allows forwarding from the secondary cluster to the primary cluster, so read-only replicas can be treated as read/write capable. Amazon ElastiCache for Redis also can replicate data across Regions, for example, for storing session data.
There is also read local/write partitioned pattern for write-heavy workloads. In this case, each item or record is assigned a home Region based on the partition key. The diagram below shows the flow as the data is partitioned by the user ID.
Active/active multi-region recovery strategy provides the quickest recovery time and least data loss. DNS TTL should be set low enough to meet recovery time objectives so that DNS resolvers will reflect changes quickly. This strategy is more complicated and more expensive.
Products
Kats - a new library from Facebook to analyze time-series data. Kats is a lightweight, easy-to-use, and generalizable framework for generic time-series analysis, including forecasting, anomaly detection, multivariate analysis, and feature extraction/embedding.
Indexing, Querying, and Full-Text Search of JSON Documents with Redis - RedisJSON allows manipulating JSON with a single atomic transaction. RedisJSON 2.0 is rewritten in Rust, fully supports JSONPath, supports Active-Active with Conflict-free Replicated Data-Type (CRDT) technology (only in Redis Enterprise). RediSearch 2.2 allows indexing, querying, and full-text search of JSON documents. It is also able to run aggregations on JSON documents.
CNCF End User Technology Radar: Multicluster Management, June 2021
Articles and blogs
What Apple’s App Tracking Changes Mean for Developers
Git Branching Strategies and The Greek Revival
Issues to Avoid When Implementing Serverless Architecture with AWS Lambda
Using Fault-Injection to Improve our new Runtime Platform’s Reliability
Doordash: Our June 19th Outage Explained - a root cause of the issue is the lack of defensive programming techniques such as load shedding and circuit breaking designed to protect distributed systems.
Audit Your Supply Chain with Amazon Managed Blockchain
How we build the Image Gallery on trivago - a dedicated Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) pipeline generates a sorted image gallery for a given accommodation considering several parameters such as the content on the image (represented by the image tag) and the quality of the image. Initial implementation on AWS was migrated to Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The most used GCP service is Dataflow: a fully managed service for Apache Beam pipelines.
Culture
Obligation and Opportunity - responsibility can’t be given, it can only be taken.
Pre-Mortem: Working Backwards in Software Design